Go (Programming Language)
Introduction to Backend
- Engineer Mindset
- Start with Why - Simon Sinek
- Why = The Purpose
- ==My purpose: Be meaningful to others and deliver ideas through technology==
- How = The Process
- ==Continuous Learning and Practice==
- What = The Result
- ==Delivering meaningful products and services to others==
- Why = The Purpose
- Start with Why - Simon Sinek
- What does a Backend Engineer really do in the industry?
- Part of software development team
- Responsible for building the server-side logic
- Data processing
- Database management
- API development
- Business logic implementation
- Performance optimization
- Security measures
- Scalability considerations
- Communication with frontend
- Communication with other services
- Components of Backend
- Server
- Database
- API
- Business / Application Logic
- 3 Levels of Backend Engineer
- Work: Make it WORK
- Good: Make it BETTER
- Fast: Make it FASTER
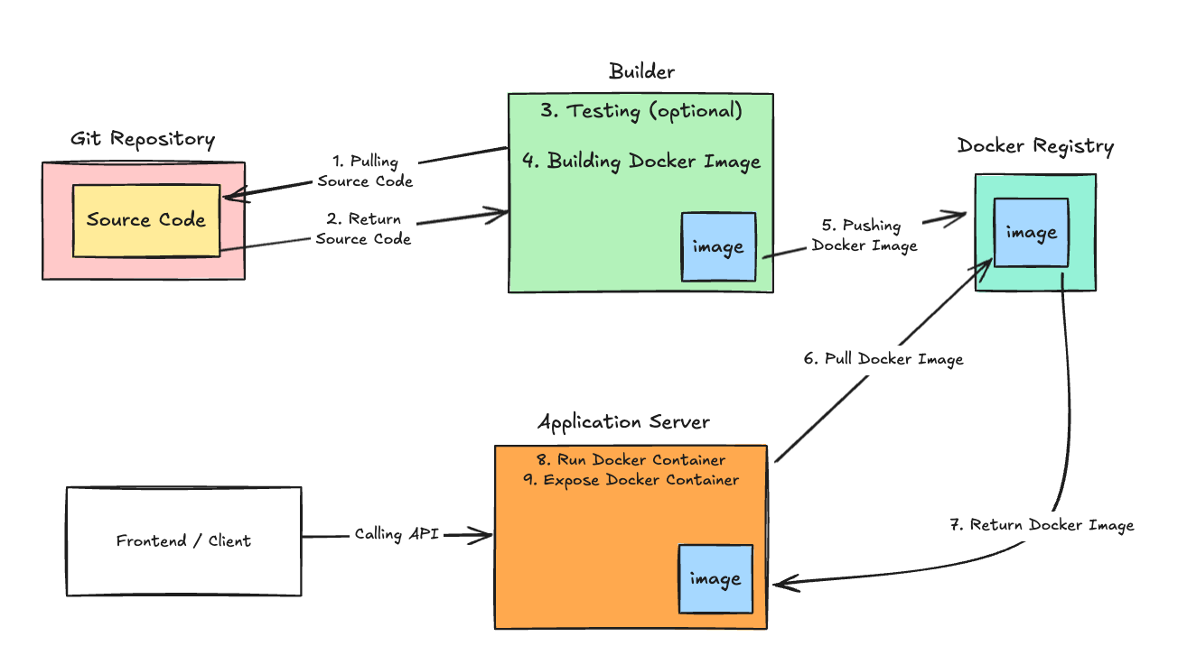
- How is an Application Deployed?
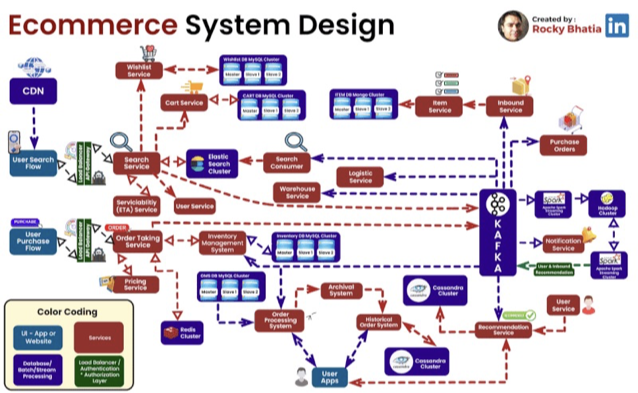
- Simple E2E System Design based on Participants' Interest
Golang Fundamentals 1
-
Setup Go
-
Go Module Initialization
go mod init github.com/yourname/myapp -
Go Project Structure
myapp/ ├── go.mod ├── go.sum ├── main.go └── internal/ ├── handlers/ │ └── user.go ├── services/ │ └── auth.go └── models/ └── user.go
-
-
Arrays
- Fixed size collection of elements of the same type
var arr [5]int arr[0] = 10
- Fixed size collection of elements of the same type
-
Slices
- Dynamic size collection of elements of the same type
slice := []int{1, 2, 3} slice = append(slice, 4)
- Dynamic size collection of elements of the same type
-
Maps
-
Collection of key-value pairs
m := make(map[string]int) m["one"] = 1 -
Access & Existence Check
value, exists := m["one"] if !exists { // handle missing key }
-
Golang Fundamentals 2
-
Structures & Interface
-
Defining Struct
type User struct { ID int Name string } -
Methods
func (u User) GetName() string { return u.Name } -
Defining Interface
type Shape interface { Area() float64 } -
Implementing Interface
type Circle struct { Radius float64 } func (c Circle) Area() float64 { return 3.14 * c.Radius * c.Radius } -
Polymorphism Example
func PrintArea(s Shape) { fmt.Println("Area:", s.Area()) }
-
-
? Go Validator
-
Pointers
-
Declaring Pointer
var p *int -
Getting Address
x := 10 p = &x -
Dereferencing Pointer
value := *p -
Modifying Value via Pointer
*p = 20
-
-
Error Handling
-
Returning Error
func divide(a, b float64) (float64, error) { if b == 0 { return 0, errors.New("division by zero") } return a / b, nil } -
Checking Error
result, err := divide(10, 0) if err != nil { fmt.Println("Error:", err) }
-
-
Recursion
-
Example of Factorial Function
func factorial(n int) int { if n == 0 { return 1 } return n * factorial(n-1) } -
Calling Recursion
fmt.Println(factorial(5)) // Output: 120
-
-
Defer, Recover, Panic
-
Defer Example
func example() { defer fmt.Println("This will be printed last") fmt.Println("This will be printed first") } -
Panic Example
func causePanic() { panic("Something went wrong!") } -
Recover Example
func safeFunction() { defer func() { if r := recover(); r != nil { fmt.Println("Recovered from panic:", r) } }() causePanic() }
-
-
? Goroutine
-
Creating a Goroutine
go func() { fmt.Println("Hello from goroutine") }() -
Synchronizing Goroutines with WaitGroup
var wg sync.WaitGroup wg.Add(1) go func() { defer wg.Done() fmt.Println("Hello from goroutine") }() wg.Wait() -
Channel
ch := make(chan int) go func() { ch <- 42 }() value := <-ch fmt.Println("Received:", value) -
Buffered Channel
ch := make(chan int, 2) ch <- 1 ch <- 2 fmt.Println(<-ch) fmt.Println(<-ch) -
Channel Direction
func sendData(ch chan<- int, data int) { ch <- data } func receiveData(ch <-chan int) int { return <-ch } -
Select Statement
ch1 := make(chan string) ch2 := make(chan string) go func() { ch1 <- "from channel 1" }() go func() { ch2 <- "from channel 2" }() select { case msg1 := <-ch1: fmt.Println(msg1) case msg2 := <-ch2: fmt.Println(msg2) } -
Mutex
var mu sync.Mutex counter := 0 mu.Lock() counter++ mu.Unlock() -
RWMutex
var rwMu sync.RWMutex data := make(map[string]string) // Writing rwMu.Lock() data["key"] = "value" rwMu.Unlock() // Reading rwMu.RLock() value := data["key"] rwMu.RUnlock() -
Once
var once sync.Once once.Do(func() { fmt.Println("This will be printed only once") })
-
Backend Server Implementation
- Deep Dive into REST API
- Building a boilerplate
- Understanding Gin
- ? What is Go Context?
- Build a CRUD application in Gin based on participants' interest
Integrating Backend Server with Database
- Gorm Introduction
- Designing Application Database (dbdiagram.io, plant/mermaid)
- Declaring Gorm Model
- Gorm Auto Migration
- Integrating backend application to PostgreSQL
Optimizing & Securing Your Application
- Knowing Proxy Design Pattern
- Knowing API Authorization
- Implementing In Memory Caching
- Introduction to Redis
- Implementing Redis
- Database Indexing
- Knowing Sharding & Partitioning
- Implementing Gin Authorization
Testing a Go Application
- Knowing what kind of testings
- Creating a mock instance
- Testing an Application with Unit Test
Microservices 1
- Introduction to Microservice
- Microservice vs Monolith
- Is monolith that bad?
- Refactoring a service to another service
- Setup API Client
- Communicating with another service
Microservices 2 & Documentation
- Knowing what is Message Broker
- Implementing RabbitMQ
- Documenting API Specification in OpenAPI
- Documenting Code
Deploying Backend
- On Premise vs Cloud
- Introduction to Docker
- Creating a Dockerfile
- Creating a docker-compose
- Running application in Docker
Logging & Recap
- Knowing Log Level
- Implementing Logging with Zap
- What else can logging do?
- Knowing OpenTelemetry
- Recap
- QnA
Status: #MOC Tags: