Memory Management
Partitioning, Placement Algorithm
- logical address - used by programs that are run above the OS so that they are easily accessible and standardized
- physical address - the physical RAM memory address
- logical address is translated to physical address using MMU
variable partition
- OS maintains information about:
- allocated partitions (for OS and other fixed programs)
- free partitions (hole) (for new processes)
pros and cons
fixed partitioning
- internal fragmentation dynamic partitioning
- external fragmentation
- compact
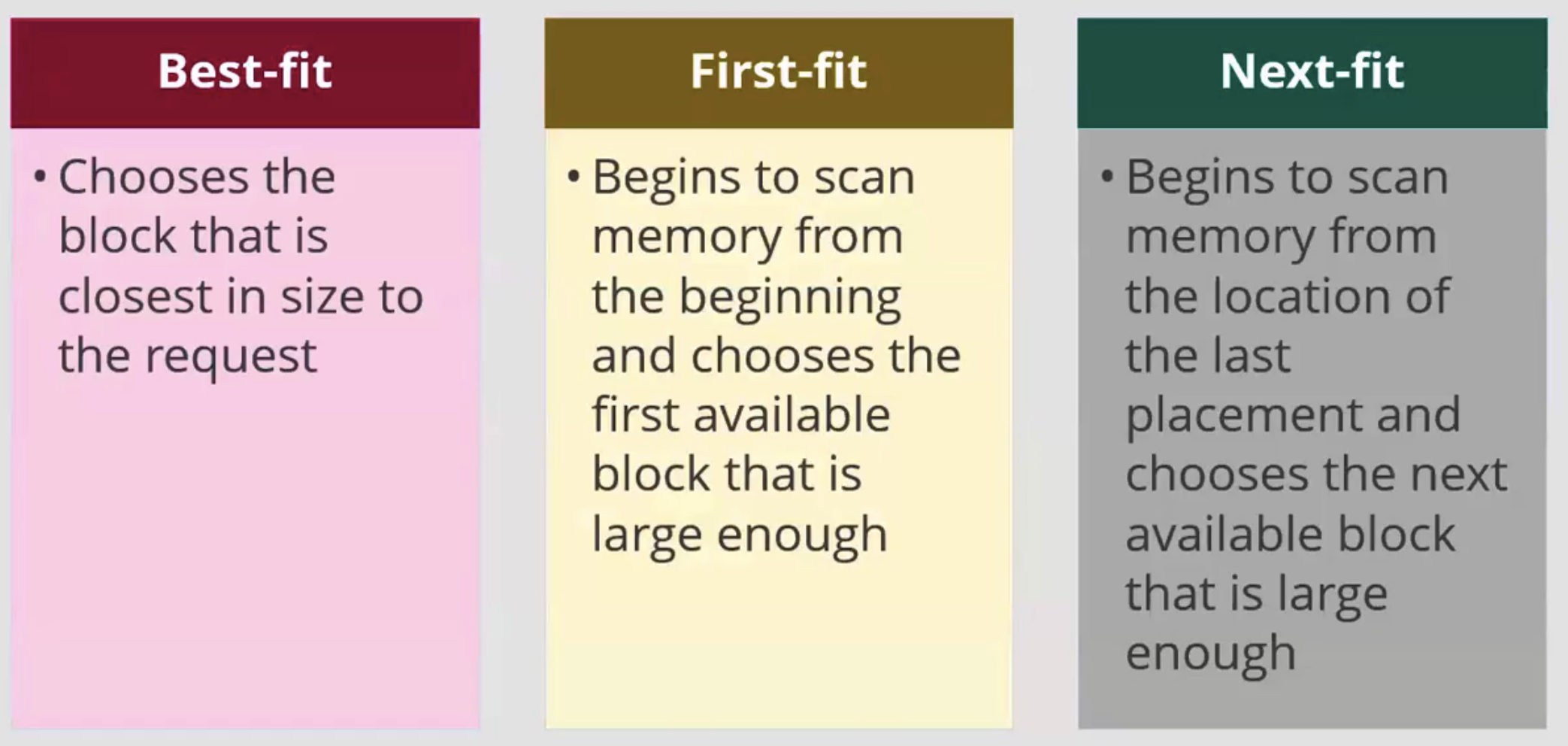
§First-fit: Allocate the first hole that is big enough
§Best-fit: Allocate the smallest hole that is big enough; must search entire list, unless ordered by size
•Produces the smallest leftover hole
§Worst-fit: Allocate the largest hole; must also search entire list
Produces the largest leftover hole
First-fit and best-fit better than worst-fit in terms of speed and storage utilization
pros and cons
- best fit
- less fragmentation
- slow to find best fit
- first fit
- fragmentation
- searching from the top
- next fit
- fragmentation same as first
- searching from the pointer
Paging
similar to File ManagementFile ManagementFile allocation algorithms (contiguous, chained, indexed) * File system resides on secondary storage (disks) * File system divides disks into several blocks of sectors (usually 512 bytes) * An allocation method refers to how disk blocks are allocated for files: * Contiguous (where the blocks that we use to store a file is ordered) * Linked (where one block is not entirely used to store data but pointers as well) * Indexed (where there is one block that stores the pointers to the data blo where a disk is divided into equally sized blocks, virtual memory is divided into several pages and physical memory is divided into multiple frames with the size of pages and frames being equal or using the same size consensus
- offset: small bytes within a frame / page (1 page = 512 byte, offset-0 until offset-511)
- same between frame and page
https://rms46.vlsm.org/2/183.pdf
- UI
- book
- zulfani
- exercises
- UI
- assignment
- responsi
Status: #idea
Tags: operating-systems > Final Exam MaterialsOperating Systems NotesDownloadMoreRAM.com - CloudRAM 2.0
study from the book bruh
Mid Exam Materials
Microprocessor
µLinux vs Linux
PThread
Multilevel Scheduling: Round Robin & FCFS
Computer Components
Interrupts
Process States
Application
Process
Deeply Embedded Systems
My OS Mid Exam Prep Notion
Other people's notes:
* Norberth's Notes
* https://www.notion.so/Operation-System-12b1620f860e80cdb47aff5eb21febb8?pvs=21
* https://www.notion.so/f97c874f97bc48ab9944243d4380d3bd?pvs=21
* https://www.notion.
References
🤓 William Stallings - Operating Systems > Chapter 11🤓 William Stallings - Operating SystemsChapter 11 Status: #reference Tags: operating-systems